Data Logger
What is a data logger?
A
data logger (or datalogger) is an electronic device that is used to store data over time, commonly known as data logging. This includes many data acquisition devices such
as plug-in boards or serial communication systems which use a computer as a real time data recording system. Nowadays, wireless transmitters are also
capable of turning a regular smart phone (or tablets) into a mobile logger.
A data logging device is often battery powered for use
where no electrical supply exists, data loggers accept one
or more sensor inputs, sampling and saving the data at a
predetermined frequency. This could be as fast as several
hundred per second or as slow as several hundred per day
(and faster and slower data loggers are available).
What is a data logger used for?
Data loggers are used wherever there is some advantage in
recording conditions over a period of time. Applications range
from obtaining a record of wind speed to
tracking temperature
in refrigerated storage containers, to monitoring flow rate at a
remote pumping station. At the end of the acquisition period
the device is retrieved and the data downloaded into a PC
for analysis. Alternatively, data loggers are available that
will wirelessly transmit measurement results to a
PC with a data logging software installed.
Find the
Data Logger for your application using our selection tool.

Learn more about Data Loggers
Types of Electric Signal available for logging
- AC Voltage/Current
- DC Voltage/Current
- Light On/Off
- Shock/Acceleration
- Bridge/Strain/Load/Pressure
- Motor On/Off
- Sound
- Dew point
- PH
- Pressure
- Temperature
- Event or State
- Process Voltage/Current
- Thermistor
- Frequency
- Relative Humidity
- Thermocouple
- Level
- RTD
Data loggers benefit users in two ways. They avoid the time
and expense of sending someone to take measurements in a
remote location, and they enable much higher data density
than is achievable through manual recording, providing higher
quality data.
Many different types of data loggers are available. They range
from single channel devices with the sensor incorporated, to
multi-channel loggers capable of acquiring from diverse
sensors for extended periods. Data logging software provides
the ability to configure acquisition parameters and format data
outputs.
How to choose a Data Logger?
Most data loggers are general purpose devices although
some are optimized for a specific type of sensor connection
and reading (temperature being the most common). A data
logging equipment may be selected for one particular task or as an
addition to an inventory of data acquisition hardware. In either
case, the needs of the intended or likely application(s) should
be considered with regard to the following capabilities.
How do data loggers work?
A general purpose multi-channel data logger will usually
accept both analog and digital inputs. Examples of analog
inputs include temperature, pH and humidity. Note that analog
inputs may be either single or double-ended (differential).
Using differential sensors halves the number of analog inputs
available. An example of this would be a
multi channel temperature logger for thermocouples.
Two examples of digital inputs are those from a
wind speed sensor or a paddlewheel-style flow sensor. Some
types of data logger are designed for specific types of sensor
input such as thermocouples or atmospheric sensors (such as
barometric pressure and humidity).

Number of Inputs
Data loggers divide into two types: those that accept only
a single sensor input (and that sensor may or may not be
integrated into the unit), and those that can be connected to
a number of sensors simultaneously. While a single channel
data logger may be sufficient for some applications the
multi-channel data logger is a more versatile device. Multichannel
loggers are available with as many as 32 inputs
(depending on how the device and sensors are configured).
However, the most commonly used type is the 4-channel
data logger as this provides a good combination of storage
capacity, battery life (where used) and compact size.
Size
In many applications space is a limitation. In those cases the size of the portable data logger may be a critical selection parameter.
OMEGA's OM-CP family of data loggers are extremely compact and include models for most input types. Submersible devices are also available for
marine and aquatic applications.
Speed/Memory
Data logging systems are available with sampling rates as high as
200 kHz while at the other end of the spectrum some can set
to sample once in 24 hours. When evaluating sampling rate
requirements note that memory capacity is a fixed number of
data points. Thus sampling at a higher frequency fills available
memory quicker. Some logger devices handle memory overload by
wrapping around and overwriting, which means older data is
lost.
Real Time Operation
In general a data logger writes each measurement point to
memory for retrieval later. However, some have the ability to
output measurement results as they are taken. Look for this
feature when it is important to see “live” measurement data.
Data Download
There are several ways of retrieving measurement results from
a data logging system. For a simple USB data logger all that’s required
is to collect it from the field and plug it into a PC. Data logging
software is available to streamline the download process and
assist with formatting for Excel® or other packages. If physically
visiting the data logger is undesirable but a wired connection
is feasible, alternatives are the serial data logger and
the
RS232 data logger. When running wires out to a remote data
logger is infeasible the solution is to use a wireless data logger
that transmits data to a receiver connected to a PC.
Key Aspects to Consider When choosing a logging system
- Input Signal
- Number of Inputs
- Size
- Speed/Memory
- Real Time Operation
Why Choose a Data Logger Over Other Types of Data Collection Instruments?
Three types of instruments are commonly used for collecting and storing data:
- Real-Time Data Acquisition Systems
- Chart Recorders
- Data Loggers
Other ways of logging measurement data are the chart
recorder and the real-time data acquisition system. Until the
development of the data logger the chart recorder was the
predominant instrument. These typically require pens and
specialized paper. Moreover, the data cannot readily be
moved into a PC for mathematical or statistical analysis.
Real-time data acquisition systems offer flexibility but also
require a direct computer connection. This limits their use in
situations where data is to be acquired in a remote location
or where portability is a consideration. For example, a realtime
data acquisition system would not be feasible in logging
temperatures inside refrigerated shipping containers.
Data logger uses
 Miniature Single Input Data Loggers
Miniature Single Input Data Loggers
Miniature single input data loggers are generally low cost devices dedicated to a specific input type. These types of data loggers
are often used in the transportation industry. A typical application would be to include a temperature data logger in a shipment of
food products to insure that the food temperature does not exceed acceptable limits. In addition to temperature miniature data loggers
are available for a large variety of input types. most input types.
 Fixed Mount Multi-Channel Data Loggers
Fixed Mount Multi-Channel Data Loggers
Fixed input loggers have a fixed number of input channels which are generally dedicated for a specific type of input.
OMEGA offers fixed input data loggers ranging from one to 8 channels.
 Handheld Multi-Channel Data Loggers
Handheld Multi-Channel Data Loggers
Handheld multi-channel loggers are commonly used in applications where the data logger is to be carried from one location to another.
They are also commonly used in benchtop or laboratory environments. In addition to storing data internally some models even contain on board
printers which can produce an immediate hardcopy of the data.
 Modular Data Loggers
Modular Data Loggers
A modular data logger is configurable and expandable through the use of plug-in modules. The modules are normally field configurable and the
user has the option of adding as many channels to satisfy the application requirement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Main Advantages of Data Logging?
A data logger provides the ability to take measurements in
any location, even during transit, without human intervention.
Furthermore, measurements can be closely spaced to capture
transient events or far apart to maximize recording duration.
Another advantage of data loggers is that
the data can then be easily transferred to a PC for analysis
and formatting. This significantly reduces the work required to
make measurements while allowing for increased data density
when needed.
Do Data Loggers Need to be Connected to a Computer?
No, some data loggers provide an option for real-time display but all OMEGA data loggers collect data independently of the computer.
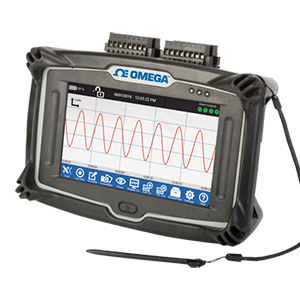
What is the Maximum Sample Rate for a Logger?
The sample rate depends on the specific model. Although most data loggers have a maximum data rate of 1 or 2 samples per second, OMEGA offers a number
of data loggers that can sample in excess of 100 samples per second.
How are the logging equipment Powered?
Most data loggers are battery powered some also offer an option for external power.
How Long Does the Battery Powered Logger Last?
The battery life depends on a number of parameters including the specific model and sample rate. In general the faster the sample rate the
shorter the battery life. Many OMEGA data loggers feature a battery life as long as ten years.
Will the Data Logger lose its Data if the Power or Battery Fails?
Most OMEGA data loggers use non-volatile memory for data storage. This means that the data will not be lost if the power fails.
How Long Can the devices Record Data?
The recording duration is dependent on the memory capacity of the data logger and the desired sample rate. To determine the duration divide the memory
capacity(number of samples the device can record) by the sample rate. As an example assume that a given data logger
can store 10,000 samples. If it is desired to record 2 samples every minute, the system can run for 10,000/2 or 5,000 minutes(about 3.5 days).
If the sample rate was cut in half(1 sample per minute), the recording period would double to 7 days.
Data Logger | Related Products
↓ View this page in another language or region ↓
 CLOSE
CLOSE














 Registradores de Dados
Registradores de Dados Enregistreurs de Données
Enregistreurs de Données Registradores de Datos
Registradores de Datos Registradores de Datos
Registradores de Datos Data Loggers
Data Loggers Dataloggere
Dataloggere Enregistreurs de Données
Enregistreurs de Données Datenlogger
Datenlogger Registratori di Dati
Registratori di Dati Data Loggers
Data Loggers Datalogger
Datalogger Data Loggers
Data Loggers Data Loggers
Data Loggers Data Loggers
Data Loggers
 データロガー
データロガー 데이터로거
데이터로거 Data Loggers
Data Loggers
 Data Loggers
Data Loggers
 Data Loggers
Data Loggers
 Data Loggers
Data Loggers
 Data Loggers
Data Loggers