 Output signals produced by temperature measurement sensors require conditioning to convert them to a form that can be used for further processing. Signal conditioning consists of:
Output signals produced by temperature measurement sensors require conditioning to convert them to a form that can be used for further processing. Signal conditioning consists of:
- Amplification
- Signal Isolation
- Error Compensation
- Linearization
- Excitation
While conditioning is essential to measurement precision, accuracy is also dependent on factors such as sensor construction and signal transmission. Impurities in the metal of sensing devices can result in temperature gradients that introduce error, and the transmission distance can affect the quality of the signal. In addition, the attributes of the measurement sensor as well as the method used for transmission can play a role in the characteristics of the signal.
Nonlinearity of Temperature Sensor Devices

An RTD is constructed of a metal, such as copper or platinum, which increases in resistance with increasing temperature. They may be either wire wound or thin film. Wire wound RTDs consist of wire coiled around a cylindrical ceramic or glass insulator. Thin film sensors have a film of material applied to a ceramic insulator which is trimmed until the resistance is the preferred value. The resistance versus temperature curve of an RTD is nonlinear. In cases where the measurement range is narrow, the nonlinearity may possibly be ignored. Over a range from 0 to 1000°C, RTDs have an accuracy of ±0.5 to 1°C.
Thermistors are made of metal oxides and may have either a negative or positive temperature coefficient. Negative temperature coefficient thermistors display a nonlinear, decrease in resistance with increasing temperatures, while positive temperature coefficient thermistors display a linear, increase in resistance with increasing temperatures. Thermistors exhibit a much greater sensitivity and signal response to changes in temperature than thermocouples or RTDs and are therefore capable of achieving higher accuracies. However, the operating temperature range of thermistors is much narrower.
Infrared temperature sensors measure temperature by focusing the amount of infrared radiation emitted from an object onto sensors, which convert it to an electrical signal. The amount of infrared energy emitted from an object is directly proportional to its temperature. Since the sensor is not in contact with the process being measured, infrared sensors are useful for very high temperature applications where other types of sensors cannot live, or for moving processes such as food cooking on a conveyor belt.
The Impact of Signal Transmission on Conditioning

Ethernet is another form of differential high speed serial transmission that supports up to 1 GB/second transmission. It usually requires a dedicated controller and is used extensively for industrial, commercial and home applications and forms the basis for today’s internet communications. Different encoding schemes are used to allow the actual measurement information to be transmitted between machines or in some cases globally using the internet infrastructure. TCP/IP is one protocol widely used within Ethernet systems, providing assured data transmissions between two devices and Ethernet connections are supported with a wide number for encryption mechanism to ensure data security.
Conclusion

 CLOSE
CLOSE










 Omega's relationship with Rutgers sprouted with their goals in substituting manual processes with an IoT solution for hands-off data collection capabilities.
Omega's relationship with Rutgers sprouted with their goals in substituting manual processes with an IoT solution for hands-off data collection capabilities.
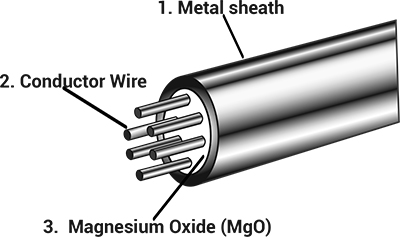 MI cables are used in high temperature or high pressure harsh environments for a good reason, here's why:
MI cables are used in high temperature or high pressure harsh environments for a good reason, here's why: